https://github.com/trey-rosius/sam_stepfunctions
Hey there, welcome to the 3rd Scenario in “Building a Step Functions Workflow “
In the first part of this series, we built a step functions workflow for a simple apartment booking scenario using the AWS Step functions low code visual editor.
In the second part of this series, we built the same workflow using CDK as IaC, Appsync and python, while invoking the step functions execution from a Lambda function.
In this post, we’ll look at how to build the same workflow, using SAM as IaC, Appsync and python.
- Install AWS Cli (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-chap-welcome.html)
- Install AWS SAM CLI(https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-sam-cli-install.html)
- AWS Account
- Any IDE of your choice. I use PyCharm
- Install python 3.8
In this post, we won’t be looking at SAM basics .So I’ll assume you’ve worked with SAM before.
If i’m wrong, I apologize. Please level up with these articles
https://github.com/aws/aws-sam-cli-app-templates
What are we trying to solve ?
So while building out a bigger system(Apartment Complex Management System) i came across an interesting problem.
I’ll assume that, most of us have reserved or booked either an apartment or hotel or flight online.
For this scenario, let’s go with apartments. So when you reserve an apartment, here’s a breakdown in the most simplest form, of the series of steps that occur after that
- The apartment is marked as reserved, probably with a status change.Let’s say the apartment status changes from vacant to reserved.
- This apartment is made unavailable for reserving by others, for a particular period of time.
- The client is required to make payment within that period of time
- If payment isn’t made within that time, the reservation is cancelled, and the apartment status changes back from reserved to vacant .
- If payment is made, then apartment status changes from reserved to occupied/paid
Building out this business logic using custom code is very possible, but inefficient.
Why ?
Because as developers, good ones for that matter, we always have to be on the lookout for tools that’ll help us carryout tasks in an efficient and scalable manner.
The series of steps outlined above, serve as a good use case for aws step functions.
- The sequence of service interaction is important
- State has to be managed with AWS service calls
- Decision trees, retries and error handling logic are required.
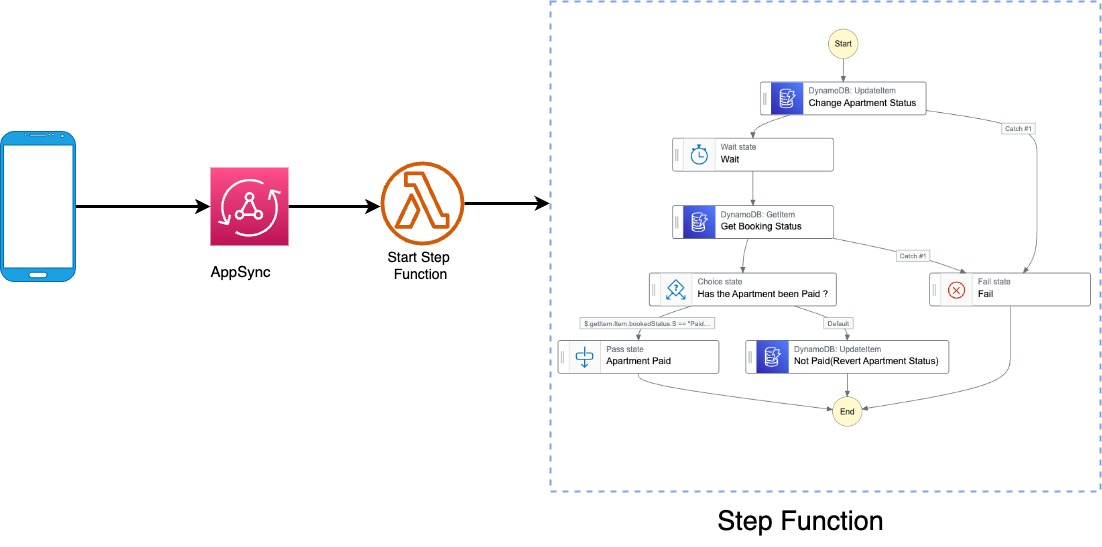
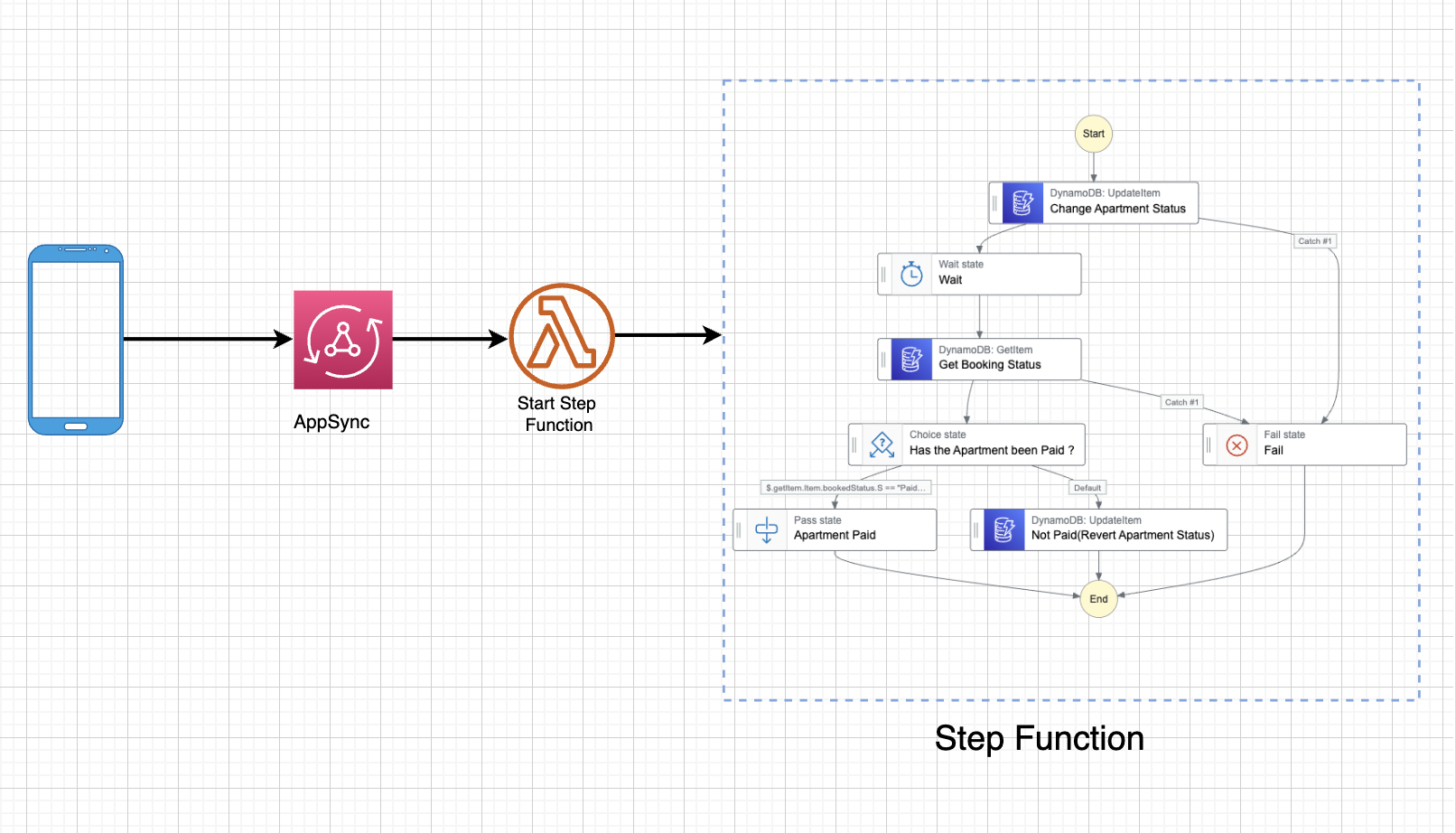 Let me quarterback this entire architecture for you please. Here’s what’s happening.
Let me quarterback this entire architecture for you please. Here’s what’s happening.
- A frontend application sends a mutation to Appsync.
- A Lambda resolver is invoked by Appsync, based on that mutation.
- Lambda gets the input from the mutation and starts a step functions workflow based on the input.
We’ll use Flutter and Amplify to build out the frontend application in the next tutorial.
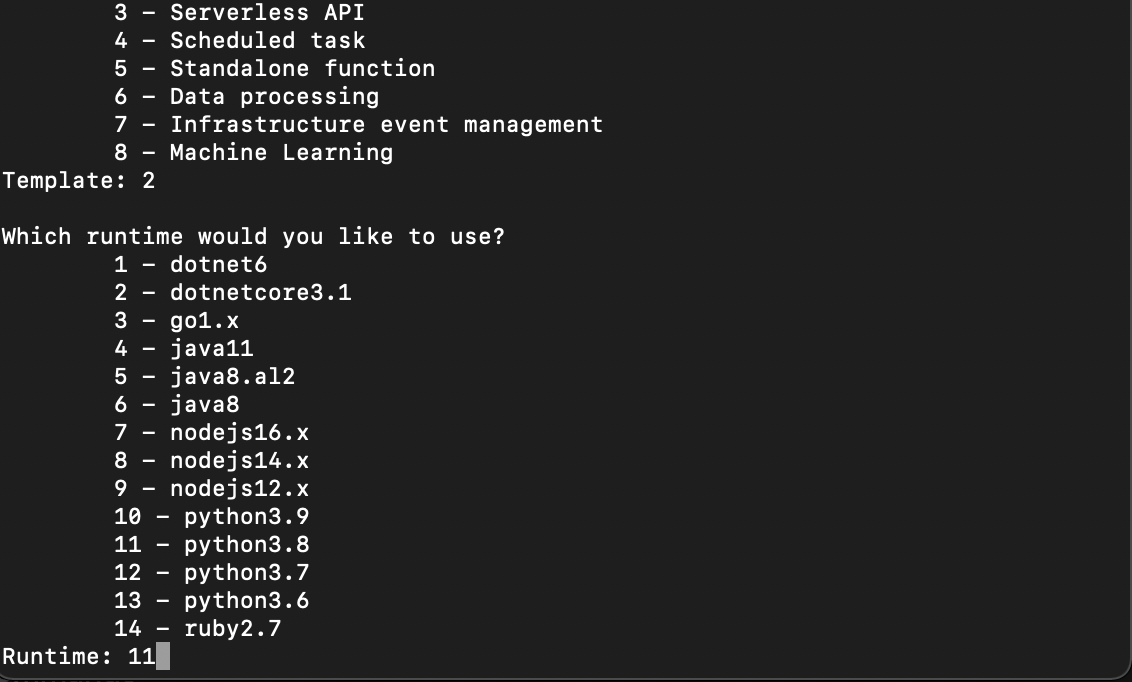
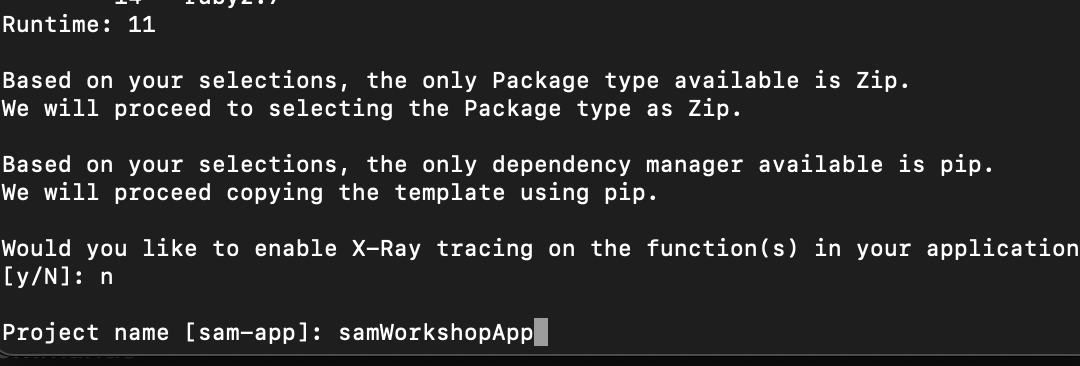
Open any Terminal/Command line interface, type in the command sam init, and follow the instructions as seen in the
screenshots.
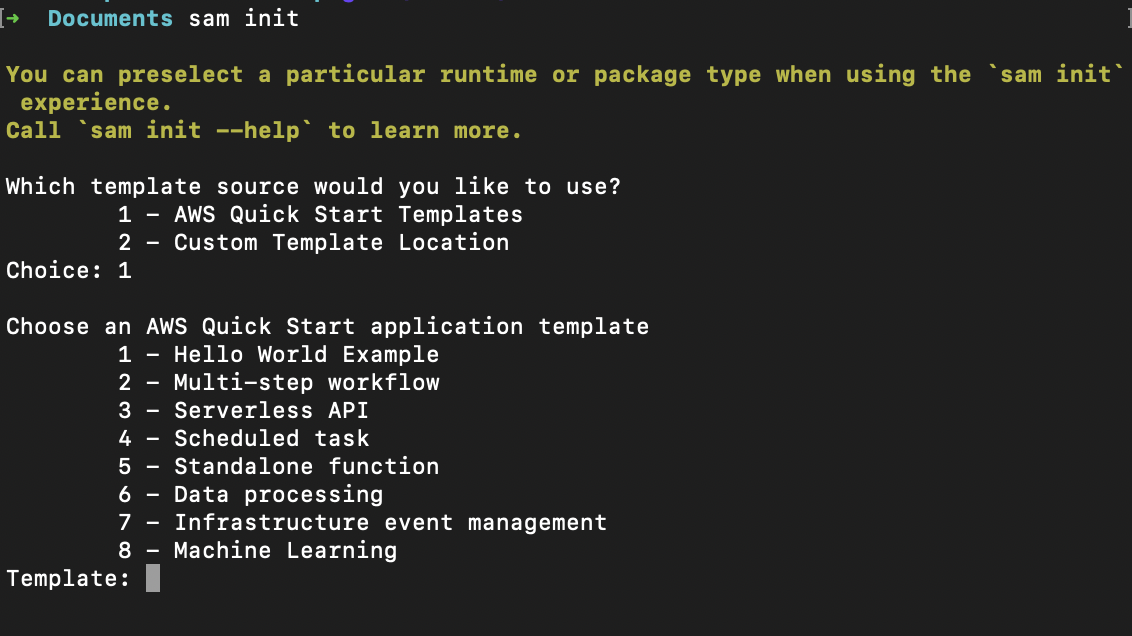
Choose python 3.8 as your runtime environment
I gave the project name samWorkshopApp
Once your application has been created, open it up in your IDE and let's proceed. I use Pycharm
Activate your virtualenv like this on mac or linux machines.
source .venv/bin/activate
If you are a Windows platform, you would activate the virtualenv like this:
.venv\Scripts\activate.bat
Once the virtualenv is activated, you can install the required dependencies.
From the root directory of the project, install all dependencies in requirements.txt by running the command pip install -r requirements.txt
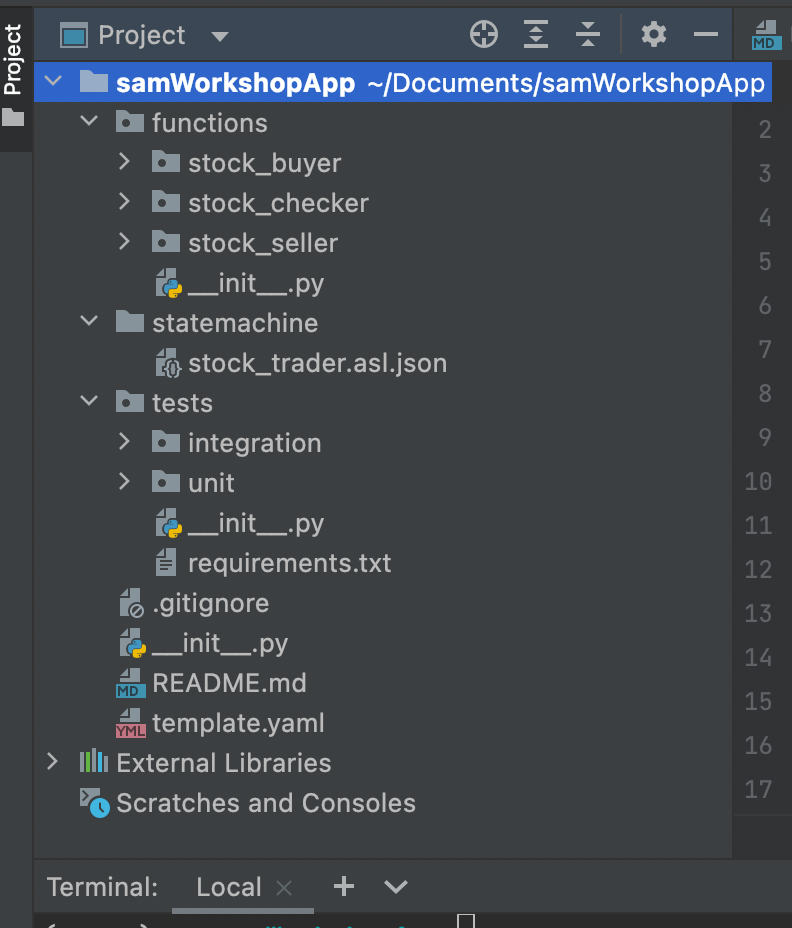
Initially, here's how my folder structure looks like
There's a couple of changes we are about to make
- inside the
functionsdirectory, delete all folders, and then create a folder called lambda. - Delete everything inside the
statemachinefolder, then create a file inside that same folder called `booking_step_functions.asl.json.
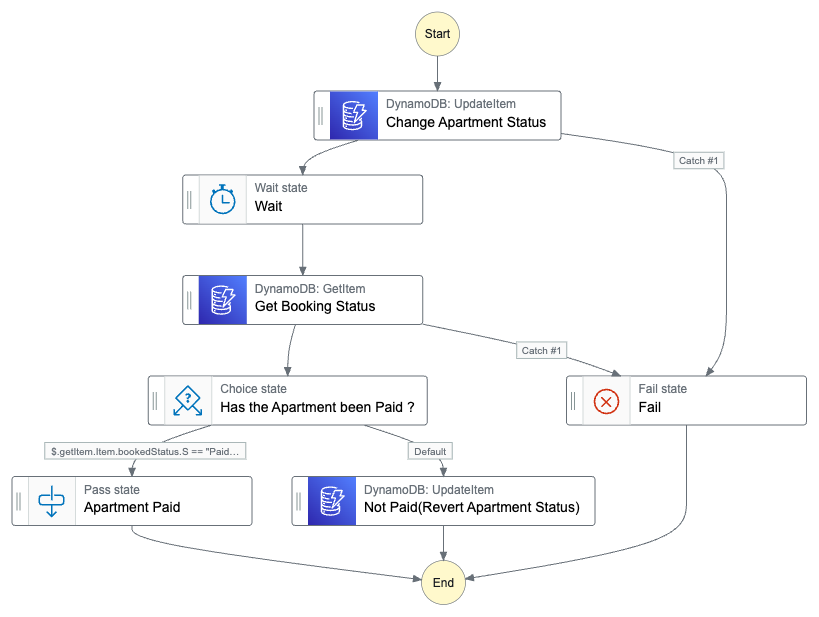
This file would contain the state machine definition for our workflow. We visually defined this workflow in part 1 of this series. Copy the ASL(Amazon States Language) for the worklflow below and paste inside the file we've created above.
{
"Comment": "A description of my state machine",
"StartAt": "Change Apartment Status",
"States": {
"Change Apartment Status": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::dynamodb:updateItem",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "apartment_workshop_db",
"Key": {
"Id": {
"S.$": "$.input.apartmentId"
}
},
"UpdateExpression": "SET #apartmentStatus = :status",
"ExpressionAttributeNames": {
"#apartmentStatus": "status"
},
"ExpressionAttributeValues": {
":status": {
"S.$": "$.input.status"
}
},
"ConditionExpression": "attribute_exists(Id)"
},
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": [
"States.TaskFailed"
],
"Comment": "Apartment Doesn't Exist",
"Next": "Fail",
"ResultPath": "$.error"
}
],
"Next": "Wait",
"ResultPath": "$.updateItem"
},
"Wait": {
"Type": "Wait",
"Seconds": 5,
"Next": "Get Apartment Status"
},
"Get Apartment Status": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::dynamodb:getItem",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "apartment_workshop_db",
"Key": {
"Id": {
"S.$": "$.input.apartmentId"
}
}
},
"ResultPath": "$.getItem",
"Next": "Has Client Made Payment ?"
},
"Has Client Made Payment ?": {
"Type": "Choice",
"Choices": [
{
"And": [
{
"Variable": "$.getItem.Item.status.S",
"StringEquals": "paid"
},
{
"Variable": "$.getItem.Item.Id.S",
"StringEquals": "1234567"
}
],
"Next": "Payment Was made."
}
],
"Default": "Payment Wasn't Made, revert."
},
"Payment Was made.": {
"Type": "Pass",
"End": true
},
"Payment Wasn't Made, revert.": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::dynamodb:updateItem",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "apartment_workshop_db",
"Key": {
"Id": {
"S": "1234567"
}
},
"UpdateExpression": "SET #apartmentStatus = :status",
"ExpressionAttributeNames": {
"#apartmentStatus": "status"
},
"ExpressionAttributeValues": {
":status": {
"S": "vacant"
}
}
},
"End": true
},
"Fail": {
"Type": "Fail",
"Error": "Apartment Doesn't Exist",
"Cause": "Update Condition Failed"
}
}
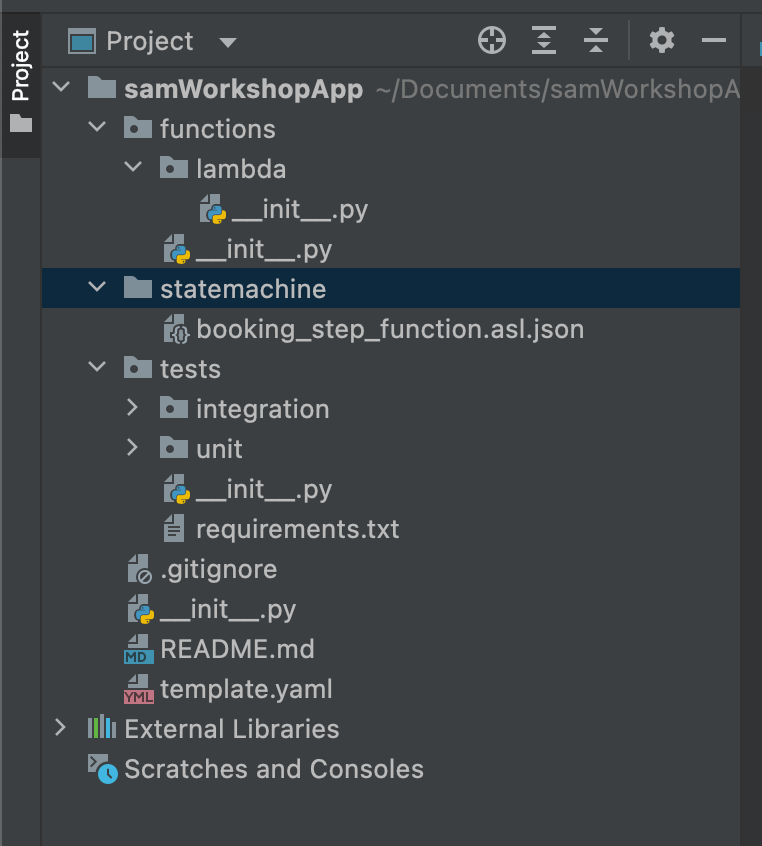
}Now, my folder structure looks like this
Remember, we have to create a graphql api, attach a schema and a database and connect a lambda resolver to it . This lambda would be responsible for invoking the step functions workflow.
Open up the template.yaml and add this GraphQl Api and API key to the resources section
SamStepFunctionsApi:
Type: "AWS::AppSync::GraphQLApi"
Properties:
Name: SamStepFunctionsApi
AuthenticationType: "API_KEY"
XrayEnabled: true
LogConfig:
CloudWatchLogsRoleArn: !GetAtt RoleAppSyncCloudWatch.Arn
ExcludeVerboseContent: FALSE
FieldLogLevel: ALL
SamStepFunctionsApiKey:
Type: AWS::AppSync::ApiKey
Properties:
ApiId: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionsApi.ApiIdWe want to see a stream of logs in cloudwatch from appsync, so let's create and assign a cloudwatch role to the GraphQL api
RoleAppSyncCloudWatch:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
ManagedPolicyArns:
- "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSAppSyncPushToCloudWatchLogs"
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Principal:
Service:
- appsync.amazonaws.comA graphql api always works with a graphql schema.
In the root directory, great a folder called graphql and inside that folder, create a file called schema.graphql.
Type in the following graphql schema into the file
type StepFunctions {
id: String!
}
type Query {
getStepFunctionsExecutions: [ StepFunctions! ]
}
input StepFunctionsInput {
id:ID!
}
type Mutation {
addStepFunctionExecution(input: StepFunctionsInput!): Boolean!
}
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
}
This schema has a single mutation addStepFunctionExecution that sends an input(id ) to a lambda resolver.
The lambda resolver uses this input to start a step functions execution.
Let's define the schema in templates.yaml under resources.
SamStepFunctionsApiSchema:
Type: "AWS::AppSync::GraphQLSchema"
Properties:
ApiId: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionsApi.ApiId
DefinitionS3Location: 'graphql/schema.graphql'Let's create a lambda function that we'll attach to a datasource and then attach that datasource to an appsync resolver
Inside the functions/lambda folder, create a file called app.py and type in the following code
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Lambda function invoked")
print(json.dumps(event))
print(json.dumps(event["arguments"]['input']))
step_function_client.start_execution(
stateMachineArn=STATE_MACHINE_ARN,
name=event["arguments"]['input']['id'],
input="{\"details\":{\"accountId\":\"1234567\",\"bookedStatus\":\"Booked\"}}",
)
return TrueFor now, this lambda function simply takes an input(id) and outputs a boolean (True).
Later on, we'll use this lambda function to start the step functions workflow.
Let's define the lambda function in template.yaml alongside its role
SamStepFunctionFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: functions/lambda/
Handler: app.lambda_handler
Role: !GetAtt lambdaStepFunctionRole.Arn
Runtime: python3.8
Environment:
Variables:
STATE_MACHINE_ARN: !Ref SamStepFunctionStateMachine
Architectures:
- x86_64 lambdaStepFunctionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Action:
- "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect: "Allow"
Principal:
Service:
- "lambda.amazonaws.com"For this application, we'll be using lambda as our datasource.
Inside template.yaml add the following code below resources
SamStepFunctionDataSource:
Type: "AWS::AppSync::DataSource"
Properties:
ApiId: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionsApi.ApiId
Name: "SamStepFunctionsLambdaDirectResolver"
Type: "AWS_LAMBDA"
ServiceRoleArn: !GetAtt AppSyncServiceRole.Arn
LambdaConfig:
LambdaFunctionArn: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionFunction.ArnSince this datasource would have to call appsync, we attach appsync service role to it
AppSyncServiceRole:
Type: "AWS::IAM::Role"
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: "Allow"
Principal:
Service:
- "appsync.amazonaws.com"
Action:
- "sts:AssumeRole"Now, we have to create a direct lambda resolver, which would connect the mutation in our schema, to the lambda datasource we created above.
Under resources in template.yaml, type in
CreateAddStepFunctionsResolver:
Type: "AWS::AppSync::Resolver"
Properties:
ApiId: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionsApi.ApiId
TypeName: "Mutation"
FieldName: "addStepFunctionExecution"
DataSourceName: !GetAtt SamStepFunctionDataSource.NameIn our workflow, we save apartment attributes to a database.Let's go ahead and create the database. It's a dynamoDB with a single primary key of ID.
SamStepFunctionsTable:
Type: AWS::Serverless::SimpleTable # More info about SimpleTable Resource: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/sam-resource-simpletable.html
Properties:
PrimaryKey:
Name: Id
Type: String
ProvisionedThroughput:
ReadCapacityUnits: 1
WriteCapacityUnits: 1A couple of steps above, we saved the step functions workflow in a file called booking_step_functions.asl.json.
We have to create a state machine resource in template.yml link to that file and do some variable substitutions like the DB name and
also provide DynamoDB read and write policies, for the update and get item dynamodb methods.
So let's go ahead and defined the step machine resource,under Resources in template.yml.
SamStepFunctionStateMachine:
Type: AWS::Serverless::StateMachine # More info about State Machine Resource: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/sam-resource-statemachine.html
Properties:
DefinitionUri: statemachine/booking_step_function.asl.json
DefinitionSubstitutions:
DDBUpdateItem: !Sub arn:${AWS::Partition}:states:::dynamodb:updateItem
DDBGetItem: !Sub arn:${AWS::Partition}:states:::dynamodb:getItem
DDBTable: !Ref SamStepFunctionsTable
Policies: # Find out more about SAM policy templates: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-policy-templates.html
- DynamoDBWritePolicy:
TableName: !Ref SamStepFunctionsTable
- DynamoDBReadPolicy:
TableName: !Ref SamStepFunctionsTable
After all variable substitutions, the booking_step_function.asl.json file looks like this now
{
"Comment": "This state machine updates the status of a booked transaction in the DB, waits for payment to be made and then updates again or passes",
"StartAt": "Change Apartment Status",
"States": {
"Change Apartment Status": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${DDBUpdateItem}",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "${DDBTable}",
"Key": {
"Id": {
"S.$": "$.details.accountId"
}
},
"ConditionExpression": "attribute_exists(Id)",
"UpdateExpression": "SET bookedStatus = :bookedStatus",
"ExpressionAttributeValues": {
":bookedStatus": {
"S.$": "$.details.bookedStatus"
}
}
},
"Next": "Wait",
"ResultPath": "$.updateResult",
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"Comment": "Items Doesn't Exist",
"Next": "Fail",
"ResultPath": "$.updateError"
}
]
},
"Wait": {
"Type": "Wait",
"Seconds": 60,
"Next": "Get Booking Status"
},
"Get Booking Status": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${DDBGetItem}",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "${DDBTable}",
"Key": {
"id": {
"S.$": "$.details.accountId"
}
}
},
"Next": "Has the Apartment been Paid ?",
"ResultPath": "$.getItem",
"Catch": [
{
"ErrorEquals": ["States.ALL"],
"Comment": "Couldn't find item",
"Next": "Fail"
}
]
},
"Has the Apartment been Paid ?": {
"Type": "Choice",
"Choices": [
{
"And": [
{
"Variable": "$.getItem.Item.Id.S",
"StringEquals": "1234567"
},
{
"Variable": "$.getItem.Item.bookedStatus.S",
"StringEquals": "Paid"
}
],
"Next": "Apartment Paid"
}
],
"Default": "Not Paid(Revert Apartment Status)"
},
"Not Paid(Revert Apartment Status)": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${DDBUpdateItem}",
"Parameters": {
"TableName": "${DDBTable}",
"Key": {
"Id": {
"S.$": "$.getItem.Item.Id.S"
}
},
"UpdateExpression": "SET bookedStatus = :bookedStatus",
"ExpressionAttributeValues": {
":bookedStatus": {
"S": "PENDING"
}
}
},
"End": true,
"ResultPath": "$.notPaid"
},
"Fail": {
"Type": "Fail"
},
"Apartment Paid": {
"End": true,
"Type": "Pass"
}
}
}
Please Grab the complete code here https://github.com/trey-rosius/sam_stepfunctions
Navigate to functions/lambda/app.py and type in this code
import boto3
STATE_MACHINE_ARN = os.environ.get("STATE_MACHINE_ARN")
step_function_client = boto3.client("stepfunctions")
sqs = boto3.client('sqs')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Lambda function invoked")
print(json.dumps(event))
print(json.dumps(event["arguments"]['input']))
step_function_client.start_execution(
stateMachineArn=STATE_MACHINE_ARN,
name=event["arguments"]['input']['id'],
input="{\"details\":{\"accountId\":\"1234567\",\"bookedStatus\":\"Booked\"}}",
)
return TrueWe import the stepfunctions class from boto3 client and use it to start a step functions execution by passing in the StateMachineArn we get from deploying the project, a unique name for the state machine execution and the state machine input
Deploy the app to your aws account using
sam build
sam deploy
Once deployment is successful, proceed to testing in appsync
Sign in to your AWS console and search for appsync. Open up appsync and click on your newly deployed appsync project.
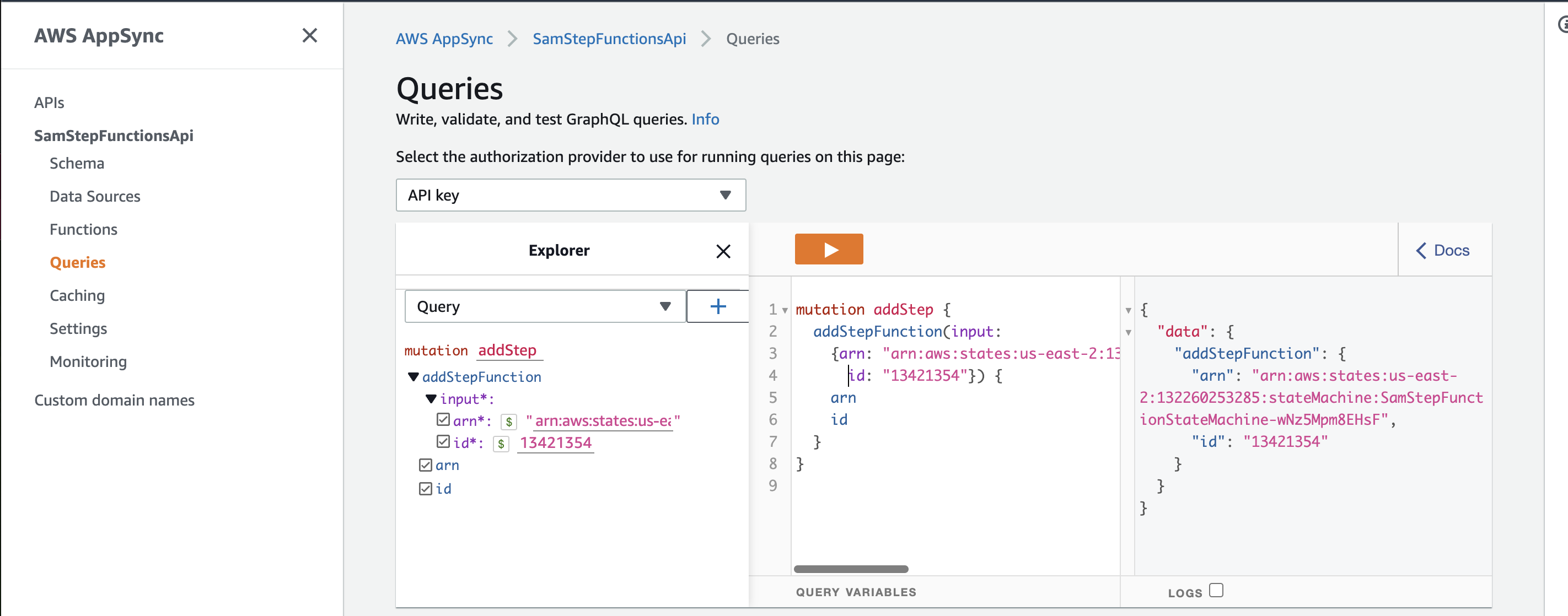
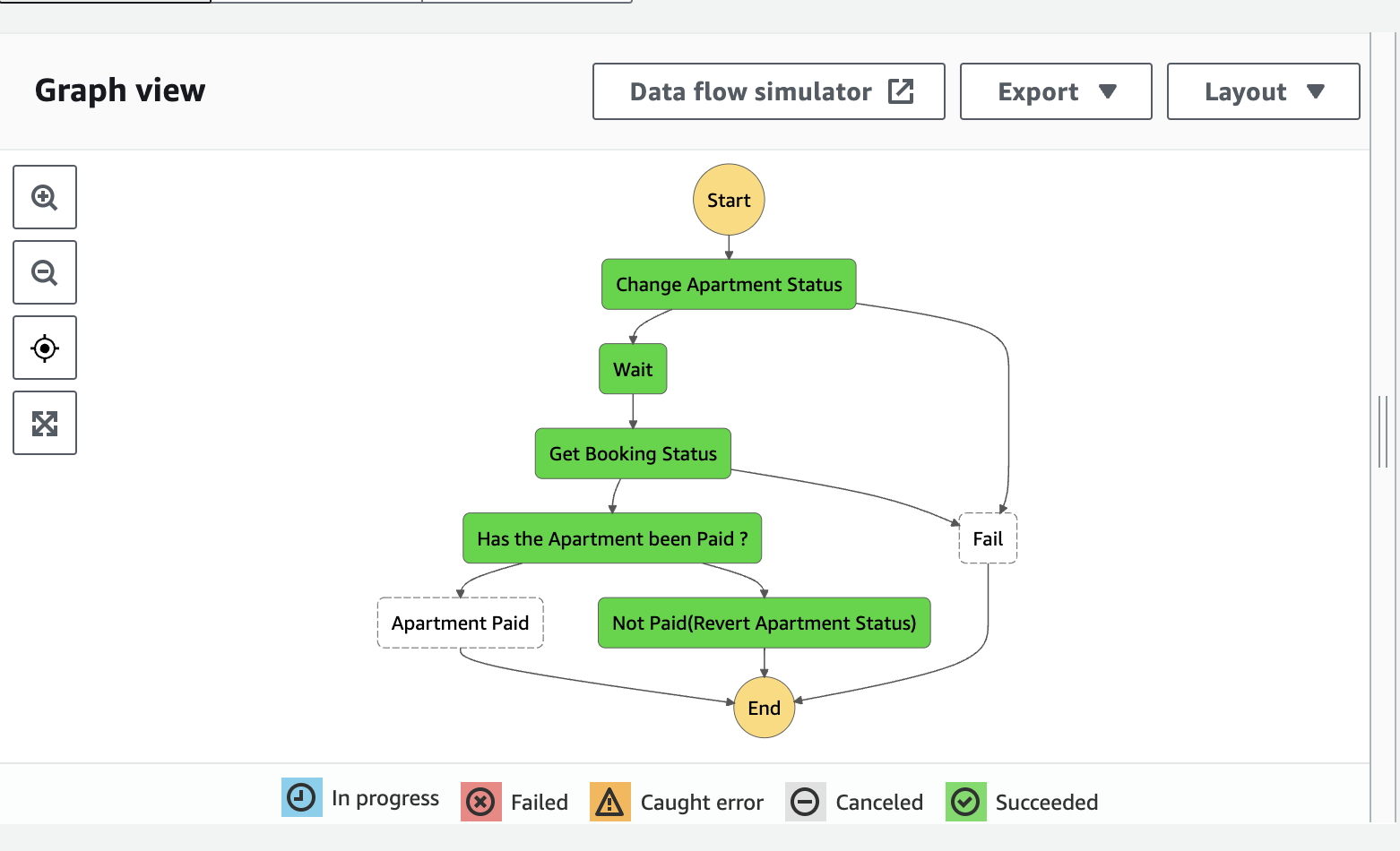
In this post, we built a step functions workflow using Appsync, SAM and Python. This workflow mimics a real life scenario of booking/reserving an apartment.
- We saw how to invoke Step functions from A lambda
- How define a state machine in a yaml file with variable substitution.
- How to use IaC to create Applications with Step functions
In the next post, we'll invoke the step functions workflow from a mobile frontend application built with amplify and flutter. Stay tuned